اثر گلخانه ای ...
این جا از شما خواهشمندم کمی به فکر کره ی زمین باشید!
نمونه اش این خرس بی چاره ... please think about earth look at this poor polar bear
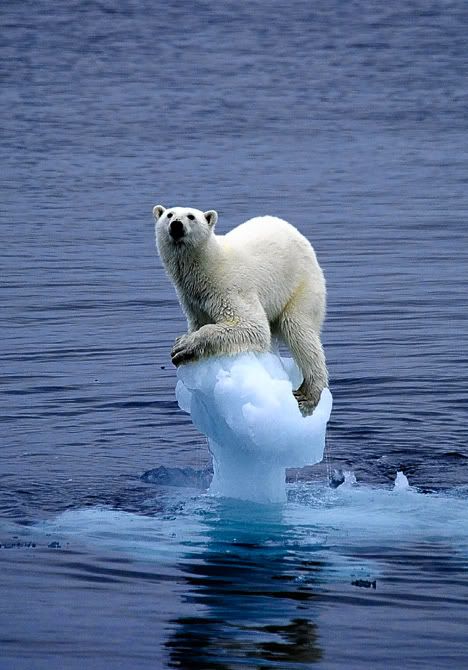

همه اش تقصیر ما انسان هاست . ما داریم کره ی خودمان را نابود می کنیم ... it's all our fault we are destroying our planet earth

و اگر به فکر این ها نیستید به فکر خودتان باشید ... if you don't think about this think about yourself

بله آب شدن یخ های قطبی اثری به جز خرس های بیچاره هم داره ...yes it has affects more than the poor bears

این هم تغییراتی که کوه پس از فقط ۱۷ سال کرده . تازه ۹ سال پیش اینجوری بود حالا کوهه چی شده!!!
لطفا کمی به فکر طبیعت باشید . سوخت های عظیمی که ما مصرف می کنیم و گازهای سی اف سی لایه ی ازن قطب جنوب رو پاره کرده اند ... this mount ha s changed a lot trough 17 years the CFC gases we used had made a hole in south poles Oson layer .

و اما چند عکس از طبیعت : and pictures from nature






حیف نیست این منظره های زیبا نابود شوند !!! ؟!؟؟
بیایید دست به دست دهیم و تا دیر نشده کره ی زمین را نجات
دهیم !
برای اطلاعات بیشتر ادامه مطالب را کلیک کنید . ممنون
lets save earth while there is still time . for more info click here .http://gtas-science.blogsky.com/
گرمشدن زمین یا گرمایش زمین (به انگلیسی: Global Warming) نام پدیدهای است که منجر به افزایش میانگین دمای سطح زمین و اقیانوسها گردیدهاست. [۱] [۲] طی ۱۰۰ سال گذشته، کره زمین به طور غیرطبیعی حدود ۰٫۷۴ درجهٔ سلسیوس گرمتر شده که این موضوع دانشمندان را نگران کردهاست.[۳] برخی از دانشمندان معتقدند که دهههای پایانی قرن بیستم، گرمترین سالهای ۴۰۰ سال اخیر بوده است. [۴] گزارشها حاکی از آن است که ۱۰ مورد از گرمترین سالهای جهان تنها از سال ۱۹۹۰ تا سال ۲۰۰۷ به ثبت رسیده است که این میزان در ۱۵۰ سال گذشته بیسابقه بوده است.[۵] به نظر میرسد فعالیتهای صنعتی در ایجاد این مشکل بسیار موثر است و به گرم شدن کره زمین کمک میکند.[۳]
از سال ۱۸۸۰ اندازهگیری دمای هوای کره زمین آغاز شدهاست و تا کنون نیز ادامه دارد. پیشبینی میشود تا سال ۲۰۱۴ زمین شاهد رکورد بیسابقه «گرم شدن» باشد. [۶] همچنین گفته میشود گرم شدن کره زمین، در سال ۲۱۰۰ باعث خشکسالی شدید، گرمای سوزان و طوفانهای وحشتناک خواهد شد. [۷]
در مورد دلایل این پدیده، یک سری از تئوریها بر تأثیر گازهای گلخانهای بر این فرآیند مبتنی است و برخی دیگر فرآیندهایی نظیر فعالیتهای آتشفشانی و زمین گرمایی و همچنین فعالیتهای خورشیدی را دلیل این پدیده میدانند. استناد این دانشمندان برای گفتههای خویش، وقوع دورههای سرد و گرم در طول مدت زمانی است که از عمر زمین میگذرد. [۲]
به عقیده بسیاری از دانشمندان با افزایش آگاهیهای عمومی، مصرف بهینه سوخت و انرژی، افزایش سطح فضای سبز و جلوگیری از تخریب جنگلها، بازیافت مواد و استفاده از انرژیهای جایگزین سوختهای فسیلی مانند باد و خورشید میتوان این پدیده و اثرات منفی آن بر زندگی بشر را کنترل کرد.
در نشست آبوهوایی کانکون مکزیک که در ماه دسامبر ۲۰۱۰ تشکیل شد ۱۹۳ کشور شرکتکننده تصمیم گرفتند تا صندوقی ۱۰۰ میلیارد دلاری را به منظور کمک به کشورهای در حال توسعه در مبارزه با گرمایش زمین تأسیس کنند.[۸] سال ۲۰۱۰ به گزارش سازمان جهانی هواشناسی گرمترین سال تاریخ زمین تعیین شده است.
علل:
هیات بینالمللی بررسی تغییرات آب و هوایی (IPCC) میگوید تغییرات جوی که در سراسر جهان مشاهده میشود به احتمال خیلی زیاد ناشی از عواملی است که بشر در آنها دست دارد. [۱۰] آکادمی ملی علوم آمریکا نیز فعالیت انسانها و تولید گازهای گلخانهای را علت اصلی این پدیده معرفی میکند.[۴]
دانشمندان با استفاده از دادههای جمعآوری شده از گیاهان، یخچالها و سایر نمونهها به این نتیجه دست یافتهاند و معتقدند که این تحقیقات بهطور قطعی تایید میکند که فعالیتهای انسانی بر آب و هوا تأثیر میگذارد. [۱۱]
ولی برخی دانشمندان معتقدند که افزایش حرارت در سالهای اخیر را میتوان به فعالیتهای خورشیدی و تابش آن نسبت داد. این گروه میگویند تصاعد دیاکسیدکربن و سایر گازهای گلخانهای کمتر از آن است که تغییرات مشاهده شده را توجیه کند.
همچنین نابودی و آتشسوزی جنگلها به عنوان یکی از دلایل گرم شدن دمای زمین مطرح شدهاست. [۱۲] درحقیقت درختان با جذب دی اکسید کربن، آن را ذخیره مینمایند که در اثر سوختن، آن را آزاد مینمایند. بنابراین آتشسوزی در جنگلها میتواند بهعنوان یکی از دلایل افزایش میزان دیاکسید کربن در اتمسفر و درنتیجه گرم شدن زمین مورد توجه قرار بگیرد. شایان ذکر است که رویداد النینیو میزان گرمای زمین را به طور موقت افزایش میدهد.
بیشک انسان در آنچه امروزه به عنوان گرم شدن جهانی از آن یاد میشود، نقش مؤثری داشته است. دخالت و برداشت بی حد و حصر نوع بشر در طبیعت باعث دگرگونی عظیمی شده که نمیتوان آن را انکار نمود. اما در طول تاریخ مسکونی شدن زمین این اولین باری نیست که این سیاره آبی به شدت گرم میشود. دورههای بیاندازه گرم و یا سرد زمین نتیجه مستقیم یا غیرمستقیم عوامل متعددی است که از قلب این سیاره آغاز شده و تا عمق فضا پیش میرود. از جمله عوامل طبیعی گرم شدن زمین میتوان به دورههای فعالیت خورشیدی، فوران آتشفشانهای بزرگ٬ چرخههای میلانکوویچ٬ گردش دماشوری اقیانوس و برخورد سیارکها یا دنبالهدارها اشاره کرد.
گازهای گلخانه ای:
تحقیقات نشان میدهند بین افزایش میزان گازهای گلخانهای موجود در اتمسفر با گرم شدن کره زمین ارتباط مستقیمی وجود دارد. [۱۴]
زمین مقداری از انرژی خورشید را جذب میکند و باقی آن را منعکس مینماید.در طی این فرآیند طول موج نور تغییر پیدا میکند. بعضی از گازهای موجود در جو زمین، این تابش خروجی را جذب میکنند. این تابش عمدتاً در محدوده فروسرخ است. مولکول گازهای گلخانهای، بسیار بیشتر از سایر گازها نور مادون قرمز را جذب میکند. جذب انرژی توسط مولکولهای گاز سبب جنبش مولکول و افزایش انرژی آن میشود. وقتی این اتفاق در مقیاس بزرگ رخ دهد، مانند این است که زمین را با یک پتو پوشاندهایم. دمای کل نواحی زمین افزایش مییابد. این پدیده اثر گلخانهای و گازهایی که در آن موثرند، گازهای گلخانهای نامیده میشوند.
پیامد ها:
برخی از دانشمندان، افزایش توفانها و گردبادهای سهمگین را یکی از نتایج گرم شدن کره زمین قلمداد میکنند. [۴] اغلب کارشناسان اقلیمی معتقدند که این روند میتواند به وقوع خشکسالیها، سیلها، بادهای گرم و توفانهای مهیبتر منجر شود اما بعضی از آنها هم بر این باور هستند که بعضی از این حوادث رخ داده علامت گرم شدن زمین نیستند چون این آشفتگی و نابسمانی ویژگی طبیعی اقلیم است.[۵] از پیامدهای دیگر بالا آمدن آب دریاها، و در نتیجه رفتن مناطق ساحلی و جزایر زیر آب و رقیقشدن آب اقیانوسها و در نتیجه افزایش بارندگی در تمام جهان است.
گرم شدن زمین باعث شدهاست که دمای داخلی یخچالهای طبیعی واقع در نقاط مختلف جهان از جمله یخچالهای واقع در شمالگان، جنوبگان و چین افزایش پیدا کند و در نتیجه با آبشدن تدریجی، حجم زیادی از ذخایر این یخچالها ذوب شود. این مساله از آنجا حائز اهمیت است که این یخچالها بخش عمدهای از ذخایر آب آشامیدنی جهان را تشکیل میدهند.[۱۶] بنابراین منابع آب آشامیدنی سالم رو به کاهش میگذارد و احتمال شیوع بیماریهایی که از طریق آب آشامیدنی ناسالم شیوع مییابند، بیشتر میشود. طبق برآوردهای سازمان بهداشت جهانی، بیماریهایی که از تغییرات اقلیمی و گرم شدن زمین ناشی میشود، هر ساله باعث مرگ و میر ۸۰ هزار نفر در کشورهای آسیایی میشود.[
منبع:http://fa.wikipedia.org
Line plot of global
mean land-ocean temperature change from 1880-2010, relative to the 1951-1980 mean. The black line is the annual mean and the red line is the 5-year
running mean. The green bars show uncertainty estimates. Source:
NASA GISSComparison of surface based (blue) and satellite based (red:
UAH; green:
RSS) records of global mean temperature change from 1979-2009. Linear trends plotted since 1982.
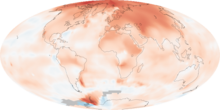
The map shows the 10-year average (2000-2009) global mean temperature anomaly relative to the 1951-1980 mean. The largest temperature increases are in the Arctic and the Antarctic Peninsula. Source:
NASA Earth Observatory [1]Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of Earth's near-surface air and oceans since the mid-20th century and its projected continuation. According to the 2007 Fourth Assessment Report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), global surface temperature increased by 0.74 ± 0.18 °C (1.33 ± 0.32 °F) during the 20th century.[2][A] Most of the observed temperature increase since the middle of the 20th century has been caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases, which result from human activities such as the burning of fossil fuel and deforestation.[3][4] Global dimming, a reduction of sunlight reaching the surface as a result of increasing atmospheric concentrations of human-made particulates, has partially countered the effects of warming induced by greenhouse gases.
Climate model projections summarized in the 2007 IPCC report indicate that the global surface temperature is likely to rise a further 1.1 to 6.4 °C (2.0 to 11.5 °F) during the 21st century.[2] The uncertainty in this estimate arises from the use of models with differing sensitivity to greenhouse gas concentrations and the use of differing estimates of future greenhouse gas emissions. An increase in global temperature will cause sea levels to rise and will change the amount and pattern of precipitation, probably including expansion of subtropical deserts.[5] Warming is expected to be strongest in the Arctic and would be associated with continuing retreat of glaciers, permafrost and sea ice. Other likely effects of the warming include more frequent and intense precipitation events, extreme weather events, species extinctions due to shifting isotherms, and changes in agricultural yields. Warming and related changes will vary from region to region around the globe, though the nature of these regional changes is uncertain.[6] As a result of contemporary increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, the oceans have become more acidic, a result that is predicted to continue.[7][8]
The scientific consensus is that anthropogenic global warming is occurring. This finding is recognized by the national science academies of all the major industrialized countries and is not rejected by any scientific body of national or international standing.[9][10][11][B] According to a recent Gallup poll, people in most countries are more likely to attribute global warming to human activities than to natural causes. The major exception is the U.S., where nearly half of the population (the largest percentage of any country) attributes global warming to natural causes.[12]
The Kyoto Protocol is aimed at stabilizing greenhouse gas concentration to prevent a "dangerous anthropogenic interference".[13] As of November 2009, 187 states had signed and ratified the protocol.[14] Proposed responses to global warming include mitigation to reduce emissions, adaptation to the effects of global warming, and geoengineering to remove greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.
Evidence for warming of the climate system includes observed increases in global average air and ocean temperatures, widespread melting of snow and ice, and rising global average sea level.[15][16][17][18] The most common measure of global warming is the trend in globally averaged temperature near the Earth's surface. Expressed as a linear trend, this temperature rose by 0.74 ± 0.18 °C over the period 1906–2005. The rate of warming over the last half of that period was almost double that for the period as a whole (0.13 ± 0.03 °C per decade, versus 0.07 °C ± 0.02 °C per decade). The urban heat island effect is estimated to account for about 0.002 °C of warming per decade since 1900.[19] Temperatures in the lower troposphere have increased between 0.13 and 0.22 °C (0.22 and 0.4 °F) per decade since 1979, according to satellite temperature measurements. Temperature is believed to have been relatively stable over the one or two thousand years before 1850, with regionally varying fluctuations such as the Medieval Warm Period and the Little Ice Age.[20]
Recent estimates by NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) and the National Climatic Data Center show that 2005 and 2010 tied for the planet's warmest year since reliable, widespread instrumental measurements became available in the late 19th century, exceeding 1998 by a few hundredths of a degree.[21][22][23] Current estimates by the Climatic Research Unit (CRU) show 2005 as the second warmest year, behind 1998 with 2003 and 2010 tied for third warmest year, however, “the error estimate for individual years … is at least ten times larger than the differences between these three years.”[24] The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) statement on the status of the global climate in 2010 explains that, “The 2010 nominal value of +0.53°C ranks just ahead of those of 2005 (+0.52°C) and 1998 (+0.51°C), although the differences between the three years are not statistically significant…”[25]
Temperatures in 1998 were unusually warm because the strongest El Niño in the past century occurred during that year.[26] Global temperature is subject to short-term fluctuations that overlay long term trends and can temporarily mask them. The relative stability in temperature from 2002 to 2009 is consistent with such an episode.[27][28]
Temperature changes vary over the globe. Since 1979, land temperatures have increased about twice as fast as ocean temperatures (0.25 °C per decade against 0.13 °C per decade).[29] Ocean temperatures increase more slowly than land temperatures because of the larger effective heat capacity of the oceans and because the ocean loses more heat by evaporation.[30] The Northern Hemisphere warms faster than the Southern Hemisphere because it has more land and because it has extensive areas of seasonal snow and sea-ice cover subject to ice-albedo feedback. Although more greenhouse gases are emitted in the Northern than Southern Hemisphere this does not contribute to the difference in warming because the major greenhouse gases persist long enough to mix between hemispheres.[31]
The thermal inertia of the oceans and slow responses of other indirect effects mean that climate can take centuries or longer to adjust to changes in forcing. Climate commitment studies indicate that even if greenhouse gases were stabilized at 2000 levels, a further warming of about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) would still occur.[
The greenhouse effect is the process by which absorption and emission of infrared radiation by gases in the atmosphere warm a planet's lower atmosphere and surface. It was proposed by Joseph Fourier in 1824 and was first investigated quantitatively by Svante Arrhenius in 1896.[34]
Naturally occurring greenhouse gases have a mean warming effect of about 33 °C (59 °F).[35][C] The major greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 36–70 percent of the greenhouse effect; carbon dioxide (CO2), which causes 9–26 percent; methane (CH4), which causes 4–9 percent; and ozone (O3), which causes 3–7 percent.[36][37][38] Clouds also affect the radiation balance, but they are composed of liquid water or ice and so have different effects on radiation from water vapor.
Human activity since the Industrial Revolution has increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to increased radiative forcing from CO2, methane, tropospheric ozone, CFCs and nitrous oxide. The concentrations of CO2 and methane have increased by 36% and 148% respectively since 1750.[39] These levels are much higher than at any time during the last 800,000 years, the period for which reliable data has been extracted from ice cores.[40][41][42][43] Less direct geological evidence indicates that CO2 values higher than this were last seen about 20 million years ago.[44] Fossil fuel burning has produced about three-quarters of the increase in CO2 from human activity over the past 20 years. The rest of this increase is caused mostly by changes in land-use, particularly deforestation.[45]
Over the last three decades of the 20th century, GDP per capita and population growth were the main drivers of increases in greenhouse gas emissions.[46] CO2 emissions are continuing to rise due to the burning of fossil fuels and land-use change.[47][48]:71 Emissions scenarios, estimates of changes in future emission levels of greenhouse gases, have been projected that depend upon uncertain economic, sociological, technological, and natural developments.[49] In most scenarios, emissions continue to rise over the century, while in a few, emissions are reduced.[50][51] These emission scenarios, combined with carbon cycle modelling, have been used to produce estimates of how atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases will change in the future. Using the six IPCC SRES "marker" scenarios, models suggest that by the year 2100, the atmospheric concentration of CO2 could range between 541 and 970 ppm.[52] This is an increase of 90-250% above the concentration in the year 1750. Fossil fuel reserves are sufficient to reach these levels and continue emissions past 2100 if coal, oil sands or methane clathrates are extensively exploited.[53]
The popular media and the public often confuse global warming with the ozone hole, i.e., the destruction of stratospheric ozone by chlorofluorocarbons.[54][55] Although there are a few areas of linkage, the relationship between the two is not strong. Reduced stratospheric ozone has had a slight cooling influence on surface temperatures, while increased tropospheric ozone has had a somewhat larger warming effect.[56]
from :www.wikipedia.org
we will save the earth!!!if you want to save the earth tell your friends about this article













آفی عزیزم ناراحت نشی ها و ولی حق چاپ بعضی مطالب که خودم ساختم و زحمت کشیدم محفوظه . این یکی اشکال نداره گوگو ولی دیگه بدون اطلاع کپی نکن .
زیبا بود
خب تو وبلاگ خودم بود . . . حالا دیگه ممنون به هر حال !!!!!!!!
سلام آفرین جون من ترمه هستم .


خیلی قشنگ بود
به وبلاگ من حتما سر بزن و نظر بده .
آفرین وبلاگ قبلی اشتباه بود به این وبلاگ سر بزن
termehe.blogfa.com
سر بزن و نظر بده .